
Pass Microsoft AZ-104 in Just 3 Days – Stress-Free, No Study Needed!
Have questions? Contact us directly on WhatsApp for quick support!
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1.
You have 5 TB of data that you need to transfer to Subscription1.
You plan to use an Azure Import/Export job.
What can you use as the destination of the imported data?
- A. a virtual machine
- B. an Azure Cosmos DB database
- C. Azure File Storage
- D. the Azure File Sync Storage Sync Service
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources shown in the following table.
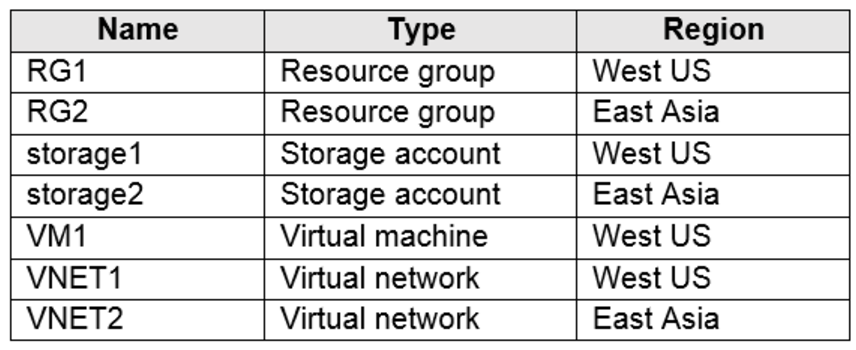
VM1 connects to VNET1.
You need to connect VM1 to VNET2.
Solution: You turn off VM1, and then you add a new network interface to VM1.
Does this meet the goal?
- A. Yes
- B. No
You have an Azure subscription that contains the resources shown in the following table.
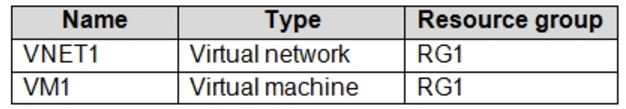
The Not allowed resource types Azure policy that has policy enforcement enabled is assigned to RG1 and uses the following parameters:
Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks
Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines
In RG1, you need to create a new virtual machine named VM2, and then connect VM2 to VNET1.
What should you do first?
- A. Remove Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines from the policy.
- B. Create an Azure Resource Manager template
- C. Add a subnet to VNET1.
- D. Remove Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks from the policy.
HOTSPOT –
You have an Azure subscription that has diagnostic logging enabled and is configured to send logs to a Log Analytics workspace.
You are investigating a service outage.
You need to view the event time, the event name, and the affected resources.
How should you complete the query? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
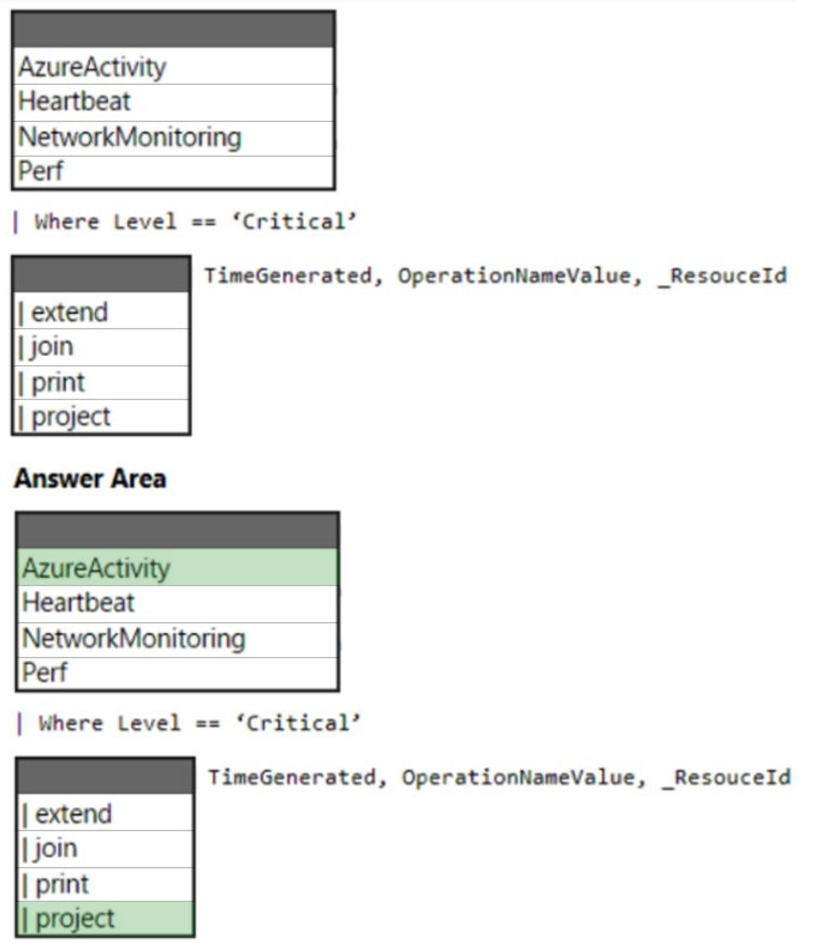
Box 1: AzureActivity –
The AzureActivity table has entries from the Azure activity log, which provides insight into subscription-level or management group-level events occuring in Azure.
Let’s see only Critical entries during a specific week.
The where operator is common in the Kusto Query Language. where filters a table to rows that match specific criteria. The following example uses multiple commands. First, the query retrieves all records for the table. Then, it filters the data for only records that are in the time range. Finally, it filters those results for only records that have a Critical level.
AzureActivity –
| where TimeGenerated > datetime(10-01-2020) and TimeGenerated < datetime(10-07-2020)
| where Level == ‘Critical’
Incorrect:
not Perf: The Perf table has performance data that’s collected from virtual machines that run the Log Analytics agent.
Box 2: | project –
Select a subset of columns: project.
Use project to include only the columns you want. Building on the preceding example, let’s limit the output to certain columns:
AzureActivity –
| where TimeGenerated > datetime(10-01-2020) and TimeGenerated < datetime(10-07-2020)
| where Level == ‘Critical’
| project TimeGenerated, Level, OperationNameValue, ResourceGroup, _ResourceId
Reference:
https://github.com/MicrosoftDocs/dataexplorer-docs/blob/main/data-explorer/kusto/query/tutorial.md
HOTSPOT –
You have an Azure subscription.
You create the Azure Storage account shown in the following exhibit.
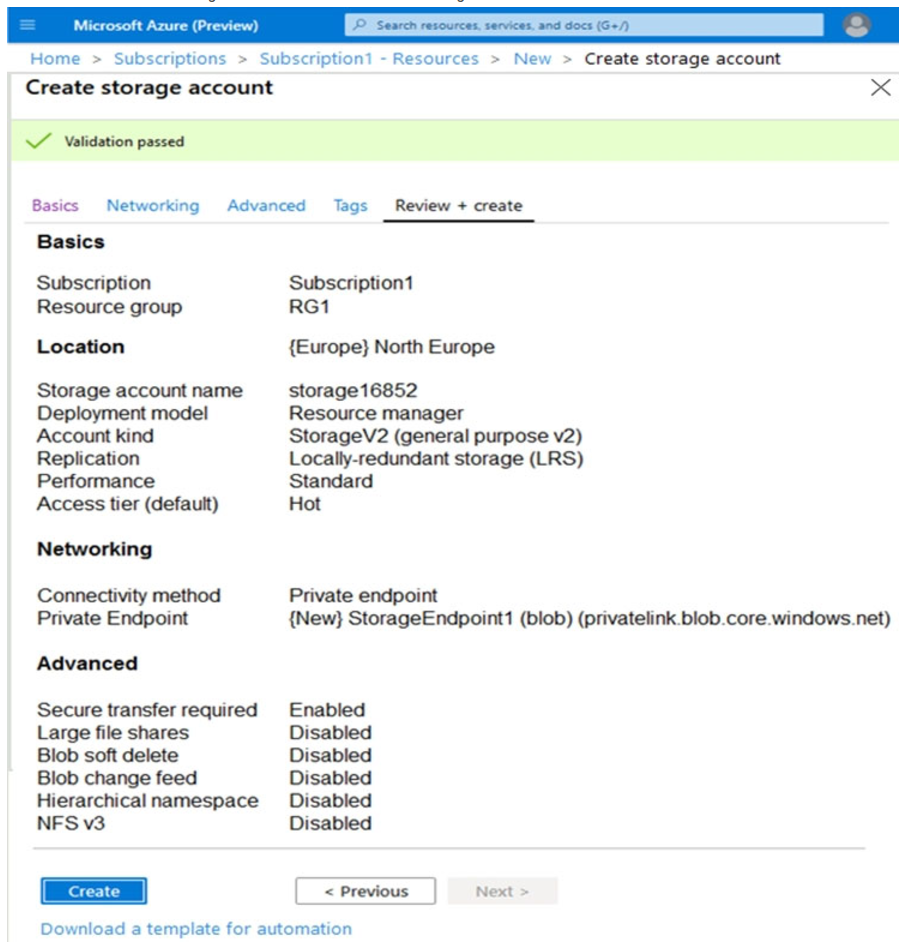
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
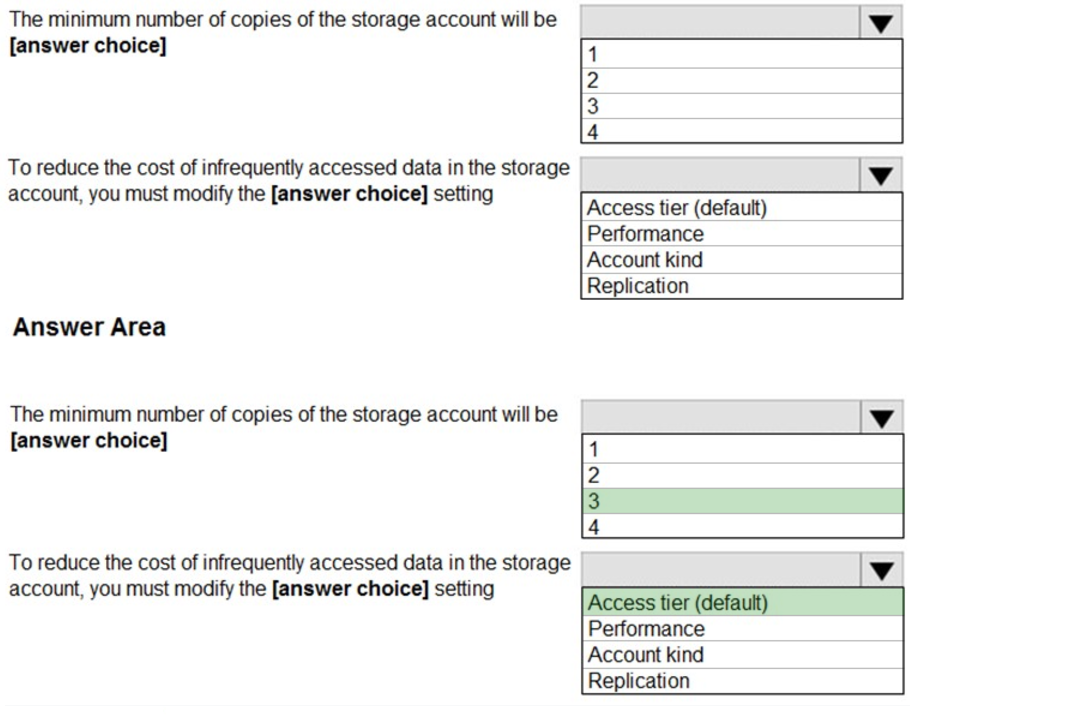
Box 1: 3 –
Locally Redundant Storage (LRS) provides highly durable and available storage within a single location (sub region). We maintain an equivalent of 3 copies
(replicas) of your data within the primary location as described in our SOSP paper; this ensures that we can recover from common failures (disk, node, rack) without impacting your storage account’s availability and durability.
Box 2: Access tier –
Change the access tier from Hot to Cool.
Note: Azure storage offers different access tiers, which allow you to store blob object data in the most cost-effective manner. The available access tiers include:
Hot – Optimized for storing data that is accessed frequently.
Cool – Optimized for storing data that is infrequently accessed and stored for at least 30 days.
Archive – Optimized for storing data that is rarely accessed and stored for at least 180 days with flexible latency requirements (on the order of hours).
Reference:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/data-series-introducing-locally-redundant-storage-for-windows-azure-storage/ https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-blob-storage-tiers
HOTSPOT –
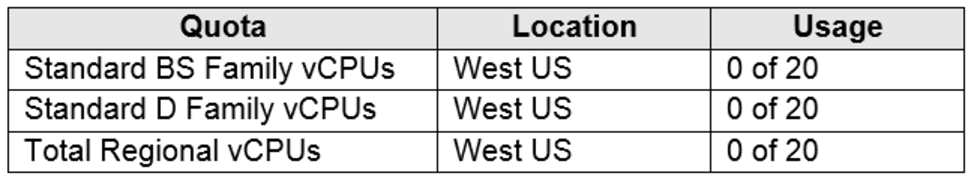
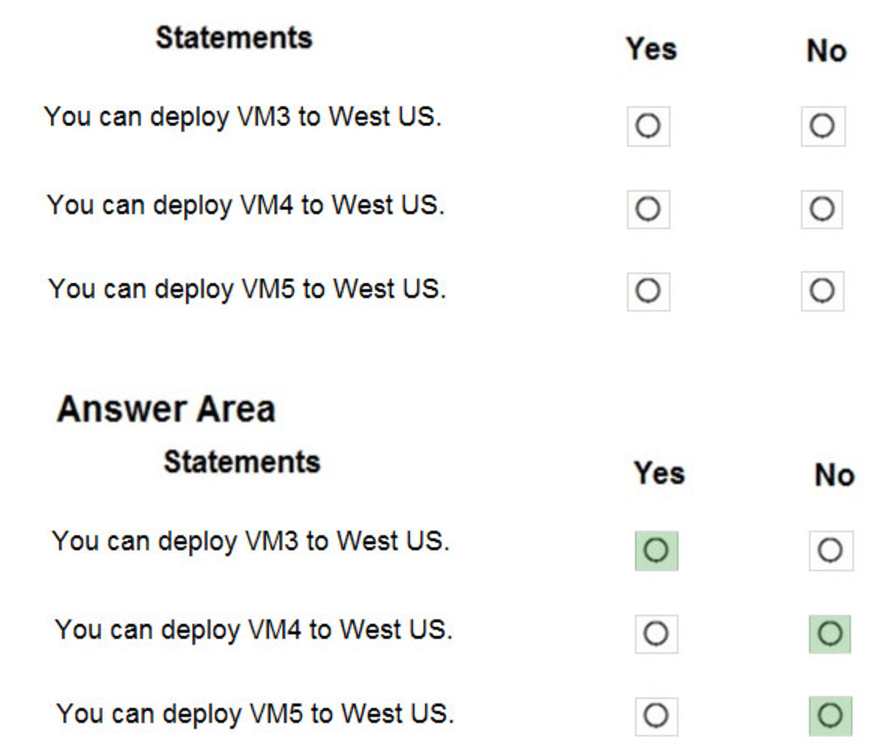
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that contains the quotas shown in the following table.
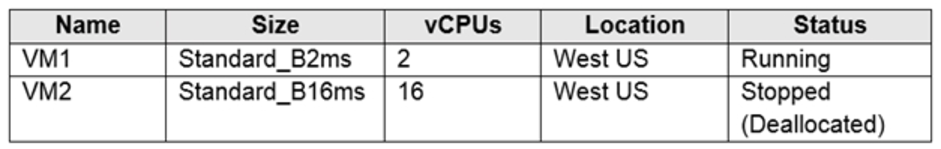
You deploy virtual machines to Subscription1 as shown in the following table.
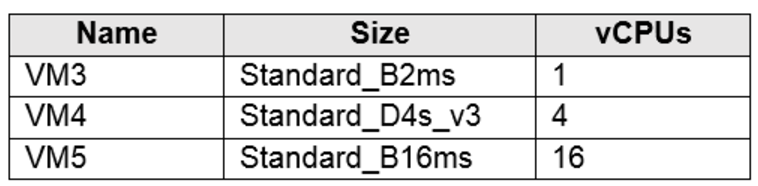
You plan to deploy the virtual machines shown in the following table.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Your company has an Azure subscription named Subscription1.
The company also has two on-premises servers named Server1 and Server2 that run Windows Server 2016. Server1 is configured as a DNS server that has a primary DNS zone named adatum.com. Adatum.com contains 1,000 DNS records.
You manage Server1 and Subscription1 from Server2. Server2 has the following tools installed:
– The DNS Manager console
– Azure PowerShell
– Azure CLI 2.0
You need to move the adatum.com zone to an Azure DNS zone in Subscription1. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
What should you use?
- A. Azure CLI
- B. Azure PowerShell
- C. the Azure portal
- D. the DNS Manager console
You have a Recovery Services vault named RSV1. RSV1 has a backup policy that retains instant snapshots for five days and daily backup for 14 days.
RSV1 performs daily backups of VM1. VM1 hosts a static website that was updated eight days ago.
You need to recover VM1 to a point eight days ago. The solution must minimize downtime.
What should you do first?
- A. Deallocate VM1.
- B. Restore VM1 by using the Replace existing restore configuration option.
- C. Delete VM1.
- D. Restore VM1 by using the Create new restore configuration option.
HOTSPOT –
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Availability Set named WEBPROD-AS-USE2 as shown in the following exhibit.
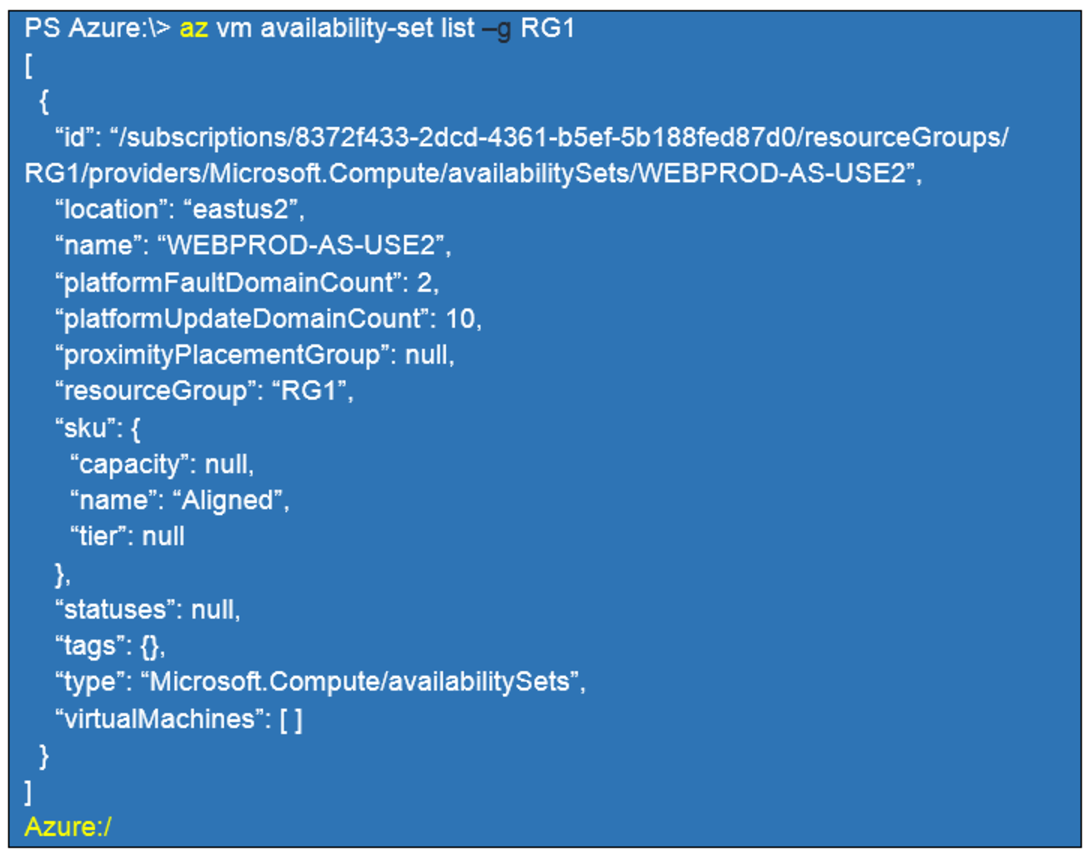
You add 14 virtual machines to WEBPROD-AS-USE2.
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
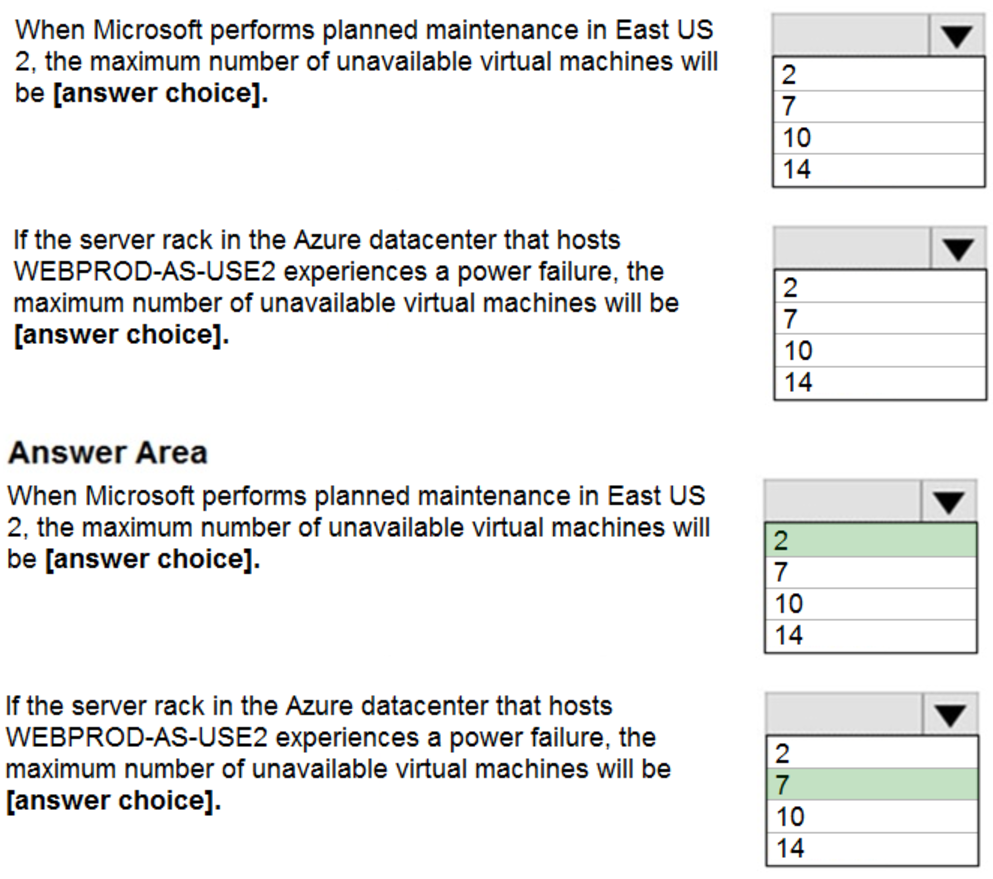
Box 1: 2 –
There are 10 update domains. The 14 VMs are shared across the 10 update domains so four update domains will have two VMs and six update domains will have one VM. Only one update domain is rebooted at a time. Therefore, a maximum of two VMs will be offline.
Box 2: 7 –
There are 2 fault domains. The 14 VMs are shared across the 2 fault domains, so 7 VMs in each fault domain. A rack failure will affect one fault domain so 7 VMs will be offline.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/manage-availability
